In this section, you will find comprehensive information about vitamins and their essential roles in maintaining overall health. Explore detailed articles on the different types of vitamins, including water-soluble and fat-soluble varieties, their sources, recommended daily allowances, and the potential health benefits of each. We provide insights into how vitamins contribute to various bodily functions, the consequences of deficiencies, and tips for ensuring adequate intake through diet and supplements. Empower yourself with knowledge to make informed choices for your nutritional needs.
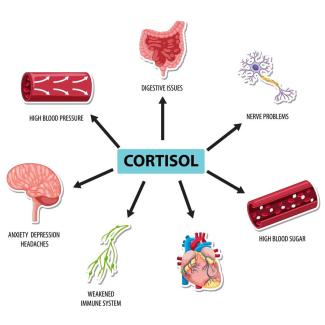
Cortisol, often referred to as the "stress hormone," plays a critical role in the body's response to stress and is essential for various physiological functions, including the regulation of metabol
Vitamin A is often considered one of the most important vitamins for healthy skin.
The management of autoimmune conditions involves a multi-faceted approach, and diet can play a significant role in helping to manage symptoms and support overall health.
Ear infections can be quite painful and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional, especially if the infection is severe, recurring, or affecting a child.
Facial wrinkles, a common sign of aging, can be effectively treated with various skincare ingredients, among which retinol is one of the most celebrated.
The desire for firm, youthful skin is universal, and maintaining skin elasticity is a key aspect of achieving this.
Vitamin E is an essential nutrient that the human body requires for various important functions.
Eggs are nutritionally rich and versatile foods with several health benefits. Let's take a detailed look at some of the key advantages of consuming eggs:
A healthy diet can play a significant role in managing and possibly preventing depression.