This comprehensive resource provides everything you need to know about minerals, essential nutrients that play crucial roles in maintaining health. Explore the different types of minerals, including macrominerals like calcium and magnesium, and trace minerals such as iron and zinc. Learn about their functions in the body, including bone health, enzyme function, and electrolyte balance. We also cover the symptoms of mineral deficiencies, recommended daily intakes, and the best food sources to ensure you're meeting your nutritional needs for optimal wellness.
Iron is crucial to the human body because it plays several essential roles in various physiological processes. Here are some of the reasons why iron is important to the human body:
Eggs have been a subject of debate when it comes to their impact on heart health due to their cholesterol content.
Eggs are widely recognized as a highly nutritious and versatile food. They are a rich source of high-quality protein, essential vitamins, and minerals, all packed in a small, low-calorie package.
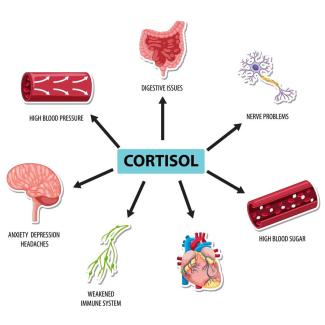
Cortisol, often referred to as the "stress hormone," plays a critical role in the body's response to stress and is essential for various physiological functions, including the regulation of metabol
Signs of magnesium deficiency: Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining dental health. It is found in various sources, including water, soil, and some foods.
Sleep apnea, a prevalent and potentially serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, affects millions of individuals worldwide.
Quinoa (pronounced KEEN-wah) is a highly nutritious and versatile grain-like crop that has gained popularity in recent years for its potential health benefits.
Potassium is an essential mineral and electrolyte that plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions.