Welcome to our comprehensive resource on internal organs, where you can explore the fascinating world of human anatomy and physiology. Our content covers a wide range of topics, including the structure, function, and health of vital organs such as the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and digestive system. Discover detailed explanations, illustrations, and the latest research findings that enhance your understanding of how these organs work together to sustain life. Whether you're a student, a healthcare professional, or simply curious, our informative articles and resources will provide valuable insights into the complexities of the human body.
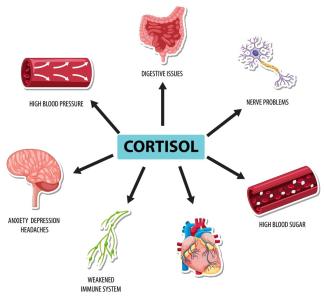
Excessive and neurotic cortisol secretion can have profound effects on the body and mind, as cortisol is a key stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands.
Blood in the urine, a condition known as hematuria, can be a cause for concern as it often signals an underlying health issue.
In traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and various folk medicine practices, the fenugreek plant has been used for a wide range of health-related purpo
Folic acid, also known as vitamin B9, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays an essential role in many physiological functions in the human body.
Probiotics and friendly microbes are microorganisms that are beneficial for human health when consumed in adequate amounts.
Signs of magnesium deficiency: Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
Triplat, also known as Greek hay or fenugreek, is a medicinal plant with a long history of use in traditional medicine. Its scientific name is Trigonella foenum-graecum.
Oregano oil is derived from the leaves and flowers of the oregano plant (Origanum vulgare or Origanum compactum). It has been used for centuries for its potential health benefits.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is one of the essential omega-3 fatty acids, which means that it must be obtained through your diet since the human body cannot synthesize it on its own.