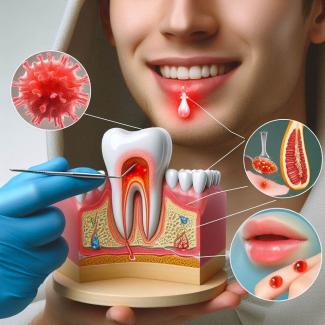
We know thousands of different species of bacteria, each with its own unique characteristics. Bacteria are microscopic organisms found in various environments, including air, water, soil, on skin, and in the digestive tracts of animals and humans. Here are some different groups of bacteria and their characteristics:
- Shape:
- Cocci: These are round bacteria, such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus.
- Bacilli: These are rod-shaped bacteria, similar to cylinders, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli).
- Spirilla: These are spiral-shaped bacteria, such as Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of cholera.
- Metabolic Pathways:
- Aerobic Bacteria: They require oxygen for their metabolism.
- Anaerobic Bacteria: They do not tolerate oxygen and can thrive in oxygen-deprived environments.
- Facultative Anaerobic Bacteria: They can survive in the presence or absence of oxygen.
- Motility:
- Flagellated Bacteria: Some bacteria have flagella (whip-like appendages) for movement.
- Sliding/Gliding Motility: Some bacteria move across surfaces by secreting slime.
- Sessile Bacteria: These bacteria remain stationary and do not actively move.
- Nutritional Habits:
- Saprophytes: They feed on decaying remains and dead organic matter.
- Parasites: They infect other organisms and cause diseases.
- Symbionts: They live in a mutually beneficial relationship with other organisms.
- Pathogenicity:
- Pathogenic Bacteria: These bacteria can cause diseases in their hosts.
- Non-pathogenic Bacteria: They are not disease-causing and serve various other roles, such as decomposing organic matter, aiding in digestion, producing vitamins, etc.
- Resistance:
- Susceptible Bacteria: These bacteria are sensitive to antibiotics and other medical interventions.
- Resistant Bacteria: They have developed resistance to antibiotics, posing a public health threat.
It's important to note that bacteria are incredibly diverse and possess numerous unique characteristics. Some are beneficial to humanity, such as bacteria that aid in food digestion, participate in food production (e.g., yogurt), and assist in environmental cleanup. At the same time, some bacteria cause severe diseases, such as tuberculosis, salmonellosis, gonorrhea, meningitis, and many others. Understanding the diversity of bacteria is crucial for the development of healthcare measures and for a better understanding of microbiological ecosystems.