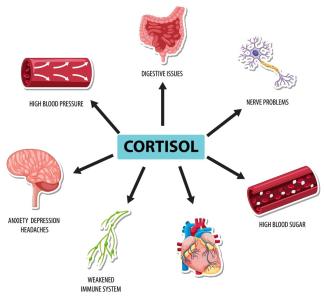
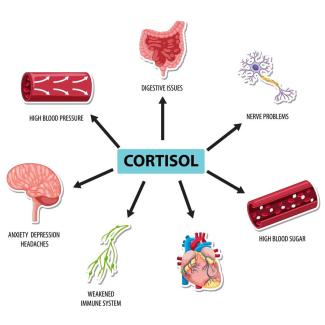
Age has a significant impact on the immune system, and understanding these changes can help you take steps to support and potentially improve its function. The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against infections and other threats. Here's a detailed explanation of how age affects the immune system and what you can do to help maintain its effectiveness:
How Age Affects the Immune System:
- Thymus Involution: One of the key changes associated with aging is thymic involution. The thymus, a primary lymphoid organ responsible for the production and maturation of T cells, gradually shrinks in size and becomes less active as we age. This results in a reduced output of naïve T cells, which are crucial for recognizing and attacking new pathogens.
- T-Cell Function: T cells are a type of white blood cell that plays a central role in cell-mediated immunity. With age, T-cell function becomes less efficient. The ability to mount a strong and coordinated immune response diminishes, which means the body becomes less effective at fighting infections.
- B-Cell Response: B cells are responsible for producing antibodies, which are crucial for recognizing and neutralizing pathogens. As people age, B cells may become less responsive, leading to a decrease in antibody production. This can affect the body's ability to fend off infections and produce a strong immune memory.
- Immunosenescence: This term refers to the overall aging of the immune system. Immunosenescence results in a less effective response to infections, a reduced capacity to adapt to new pathogens, and a higher susceptibility to chronic diseases.
- Inflammation: Chronic, low-grade inflammation, often referred to as "inflammaging," becomes more prevalent with age. While inflammation is a part of the immune response, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues and weaken the overall effectiveness of the immune system.
Ways to Support and Improve Your Aging Immune System:
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: A balanced and nutrient-dense diet is essential for supporting the immune system. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. Specific nutrients, like vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, and antioxidants, are known to be beneficial for immune health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity has been shown to improve immune function by enhancing circulation and promoting the movement of immune cells. Aim for regular, moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is crucial for the regeneration of the immune system. Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of restorative sleep each night.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to manage stress effectively.
- Vaccination: Consider receiving vaccinations that are recommended for older adults, such as the annual flu shot, pneumococcal vaccines, and shingles vaccine. Vaccination helps prevent severe infections.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system. If you smoke, quitting is strongly advisable, and limiting alcohol intake is important for immune health.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help identify and address potential health issues early, contributing to a healthy immune system.
- Hand Hygiene and Infection Prevention: Practicing good hand hygiene, using hand sanitizers, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and green tea, can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation associated with aging.
- Maintain Social Connections: Social interaction, a strong support system, and a positive outlook on life can have a favorable impact on your overall health and immune function.
While age-related changes in the immune system are inevitable, leading a healthy lifestyle, staying up to date with vaccinations, and following preventive measures can significantly bolster immune function and reduce the risk of infections and diseases as you age. It's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations and guidance on maintaining a robust immune system as you get older.